How to Read the Performance Curve of Diaphragm Pumps?
Understanding the performance curve of micro diaphragm pumps is crucial for a deeper understanding of Miniature diaphragm pumps. The performance curve is a key tool that contains a series of key information to evaluate whether the pump can provide the required flow rate under specific pressure differential conditions, helping engineers and operators understand the performance of diaphragm pumps under different operating conditions.
I. What is a Performance Curve?
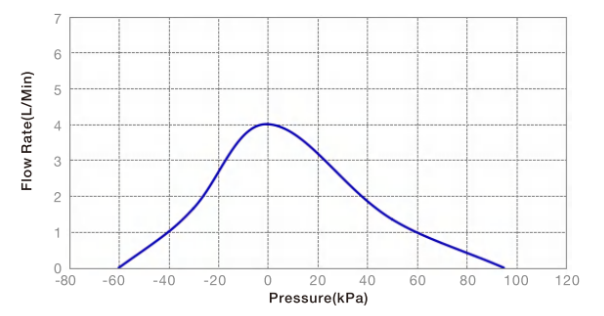
Performance Curve of TM30-A12-B01-P9504
The performance curves graphically demonstrate the performance of the Miniature diaphragm pumps at different operating points.
1.The horizontal axis of the curve represents the pressure, which is usually measured in KPa, bar or MPa, while the vertical axis represents the flow rate, which is usually measured in L/min.
2.Air pumps are divided into pressure pumps and vacuum pumps. Depending on the application, the performance curve may have a vertical split line that separates the curve into pressure applications and vacuum applications.
The left side of the vertical line marks the vacuum application, and the pressure values on the horizontal axis represent the vacuum level at the inlet side of the pump in this application scenario, with the outlet pressure of the pump always maintained at a constant level of 1000 mbar (ambient pressure).
The right side of the vertical line marks the pressure application, and the values on the horizontal axis represent the pressure at the outlet side of the pump, which indicates the relative pressure with the ambient pressure is maintained at 1000 mbar.
3.On the horizontal axis, the two furthest data points represent the two extremes that the pump can achieve, i.e. the ultimate vacuum (on the left) and the maximum pressure (on the right). On the vertical axis, the highest data point represents the maximum flow rate that the pump can achieve.
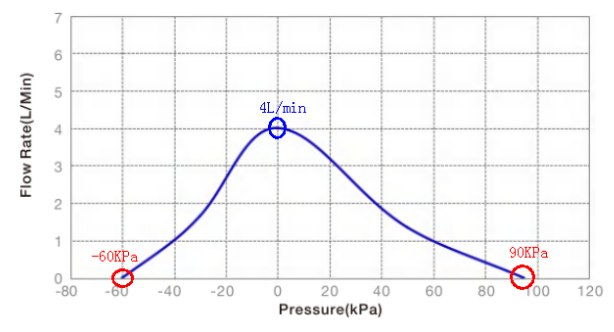
Performance Curve of TM30-A12-B01-P9504
4.In addition to the flow rates, the performance curve of some models also indicates that it should be avoided to exceed certain pressure ranges during continuous operation. Although from a technical perspective, the TF30-A12-C01-W104 can achieve a head of over 20M, this range is not included in its performance curve because it exceeds its allowable working pressure range. It is allowed to have pressure exceeding the standard for a short period of time to impact the pump, but if it works for a long time beyond the standard pressure range, the service life of the pump will be greatly shortened.
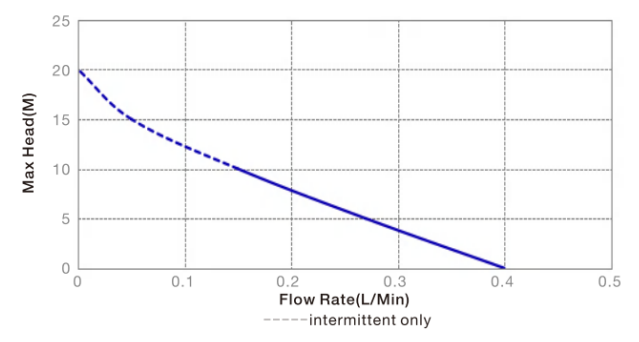
Performance Curve of TF30-A12-C01-W104
II: How to Read the Performance Curve of Micro Diaphragm Pumps
To use the pump performance curve:
1.Firstly, you need to clarify whether your application falls into the vacuum or pressure category, and identify the flow rate that meets the application requirements as well as the pressure differential between the pump inlet and outlet.
2.Then, find the point on the performance curve that corresponds to these values to ensure that the pump can operate efficiently.
3.During the pump selection process, you may also need to consider the power consumption of the pump at that point of operation and other factors that depend on the specific application.
III. Key Points of the Performance Curve
Limit Points: The two furthest points on the performance graph indicate the lowest vacuum (left) and the highest pressure (right) that the pump is capable of achieving. These points may not be shown in every graph as they depend on the type of pump and the permissible operating range.
Maximum: The highest intersection point of the curve represents the no-load flow rate of the pump, indicating that there is no restriction or pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the pump. This is the maximum flow rate of the pump.
Application matching: By identifying whether a specific application is vacuum or pressure and finding the point that corresponds to the required flow rate and differential pressure, ensure that the pump can operate effectively at that operating point.
IV. The Importance of Performance Curves
The performance curve is a key tool in the selection and operation of diaphragm pumps, helping to optimize the efficiency and performance of the system. Different models of pumps have different performance curves due to their internal operating principles, so a proper understanding of these curves is critical to the effective selection and operation of the pump. You can avoid overloading or running the pump in inappropriate ranges, extending its life and saving costs.
Interpreting diaphragm pump performance curves can be challenging, but is critical to the proper selection and operation of your pump. As experts in diaphragm pumps, we understand the complexities of performance curves and are ready to provide you with professional assistance to ensure that the pump you select best meets your needs.
Whether you are looking for a diaphragm pump for a specific application or would like to gain a deeper understanding of what performance curves mean, we are always ready to provide you with professional advice and support.


